Please select the type of consultation
AnyShare
AnyBackUp
AnyRobot
Please select the type of consultation

We will contact you within 24 hours.

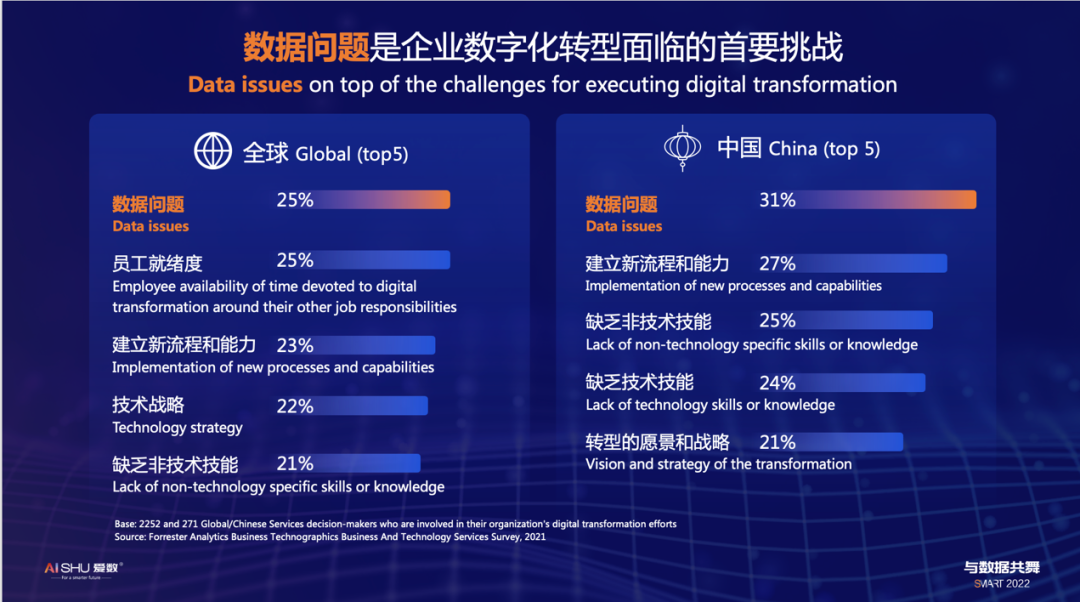


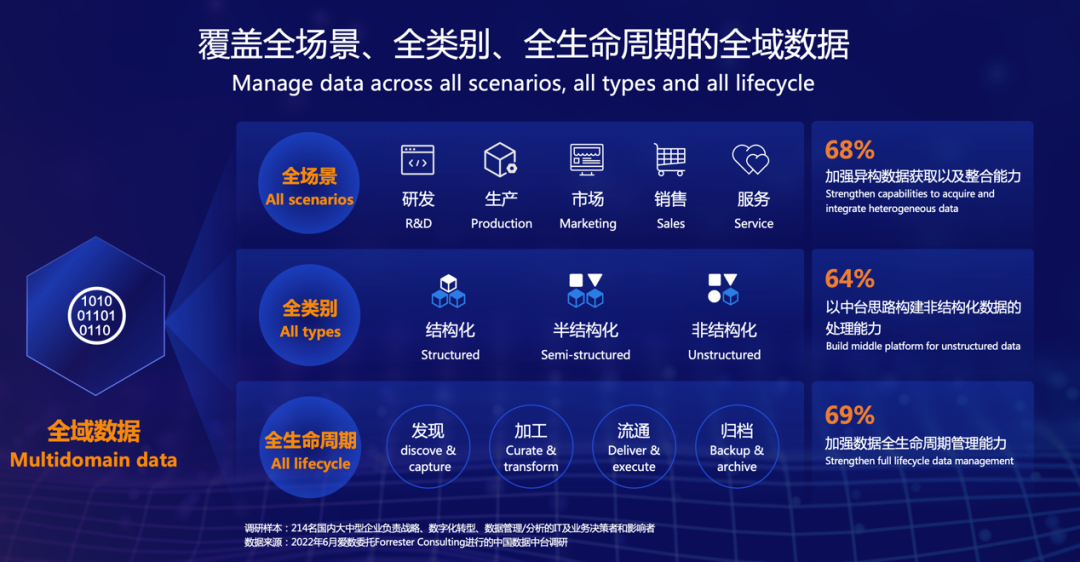

support@aishu.cn(Japan & Korea)